만족
[Blockchain] js로 이해하는 블록체인의 작업 증명 (POW; Proof Of Work) 본문
[Blockchain] js로 이해하는 블록체인의 작업 증명 (POW; Proof Of Work)
BlockChain/이론 Satisfaction 2021. 9. 13. 22:14이전 포스트에서 계속되는 내용이다.
https://satisfactoryplace.tistory.com/285
[Blockchain] js로 이해하는 블록체인의 기본 구조
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zVqczFZr124&list=LL&index=4&ab_channel=SimplyExplained 위 영상을 참고하여 작성된 포스트임을 먼저 밝힌다. 블록체인이란? 여러 개의 블록이 체인처럼 엮여있는 형상을 가지..
satisfactoryplace.tistory.com
또한 이 포스트는 아래 영상을 참고하여 만들어졌다.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HneatE69814&ab_channel=SimplyExplained
POW (Proof of Work)
POW는 비트코인에서 블록의 생성 속도를 제어하기 위해 만들어졌다.
블록의 생성 속도가 빠르다면, 공격자가 블록을 무더기로 생성하여
실제 블록체인에 가짜 블록이 입력될 수 있기 때문에
새로운 블록을 만들기 위해 걸리는 시간을 고의적으로 늘리는 방법을 사용한다.
시간이 오래 걸린다는 뜻은 많은 연산을 요구하여 많은 컴퓨팅 자원을 요구한다는 의미이다.
POW: Nonce
const SHA256 = require("crypto-js/sha256");
//Block
const Block = function (index, timestamp, data, prevHash = "") {
this.index = index;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.data = data;
this.prevHash = prevHash;
this.hash = "";
};
Block.prototype.calcHash = function () {
//index, prevHash, timestamp, data를 입력으로 해시값을 계산한다
return SHA256(
this.index + this.prevHash + this.timestamp + JSON.stringify(this.data)
).toString();
};위 코드는 이전 포스트에서 작성한 코드이다.
여기에서 새로운 블록을 만드는 속도를 늦추려면 어떻게 해야 할까?
비트코인에서는 해시할 때 Nonce라는 정수값을 추가하여 해시하게 하고,
해시값의 시작이 Difiiculty(난이도)개의 0으로 시작하는 해시값을 구해야 한다.
이것을 채굴(Mining)이라고 부르며, 구현은 다음과 같다.
const SHA256 = require("crypto-js/sha256");
//Block
const Block = function (index, timestamp, data, prevHash = "") {
this.index = index;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.data = data;
this.prevHash = prevHash;
this.hash = this.calcHash();
this.nonce = 0;
};
//이제 해시값을 계산할 때 nonce도 추가로 포함한다
Block.prototype.calcHash = function () {
//index, prevHash, timestamp, data, nonce를 입력으로 해시값을 계산한다
return SHA256(
this.index +
this.prevHash +
this.timestamp +
JSON.stringify(this.data) +
this.nonce
).toString();
};
//블록 생성 (채굴)
Block.prototype.mining = function (difficulty) {
const start = new Date();
//difficulty개의 0으로 시작하는 hash가 발생될 때 까지 해시를 반복한다
while (
this.hash.substring(0, difficulty) !== Array(difficulty).fill("0").join("")
) {
this.nonce++;
this.hash = this.calcHash();
}
const end = new Date();
//조건을 만족했을 때 nonce 값 출력
//이 때 nonce는 해시를 한 횟수와 동일하다
console.log("block is mined", this.nonce);
//걸린 시간 출력
console.log("ellipsed time is ", end.getTime() - start.getTime(), "ms");
};이전까지는 블록의 hash를 계산할 때 "이전 블록의 해시+ 현재 블록의 내용"에 대해 한 번만 해시하면 됐지만,
이제는 추가로 nonce값을 포함해 해싱하며, difficulty개의 0으로 시작하는 해시값이 나올 때 까지 nonce를 증가시키며 반복한다.
이제 블록체인에 블록을 추가할 때, 이 mining과정을 거치도록 변경해 보자.
//Blockchain
const Blockchain = function () {
this.chain = [this.createGenesisBlock()];
this.difficulty = 2;
};
//...
Blockchain.prototype.addBlock = function (newBlock) {
//새로운 블록이 생성되면 가장 최근 블록의 해시값을 새로운 블록의 prevHash에 복사한다
newBlock.prevHash = this.getLatestBlock().hash;
newBlock.mining(this.difficulty);
//해시 계산이 완료되면 블록체인에 연결시킨다
this.chain.push(newBlock);
};
자, 이제 POW가 적용된 블록체인을 한 번 테스트 해 보자.
테스트
const SHA256 = require("crypto-js/sha256");
//Block
const Block = function (index, timestamp, data, prevHash = "") {
this.index = index;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.data = data;
this.prevHash = prevHash;
this.hash = this.calcHash();
this.nonce = 0;
};
Block.prototype.calcHash = function () {
//index, prevHash, timestamp, data를 입력으로 해시값을 계산한다
return SHA256(
this.index +
this.prevHash +
this.timestamp +
JSON.stringify(this.data) +
this.nonce
).toString();
};
//블록 생성
Block.prototype.mining = function (difficulty) {
const start = new Date();
//difficulty개의 0으로 시작하는 hash가 발생될 때 까지 해시를 반복한다
while (
this.hash.substring(0, difficulty) !== Array(difficulty).fill("0").join("")
) {
this.nonce++;
this.hash = this.calcHash();
}
const end = new Date();
//조건을 만족했을 때 nonce 값 출력
//이 때 nonce는 해시를 한 횟수와 동일하다
console.log("block is mined", this.nonce);
//걸린 시간 출력
console.log("ellipsed time is ", end.getTime() - start.getTime(), "ms");
};
//Blockchain
const Blockchain = function () {
this.chain = [this.createGenesisBlock()];
this.difficulty = 5;
};
Blockchain.prototype.addBlock = function (newBlock) {
//새로운 블록이 생성되면 가장 최근 블록의 해시값을 새로운 블록의 prevHash에 복사한다
newBlock.prevHash = this.getLatestBlock().hash;
newBlock.mining(this.difficulty);
//해시 계산이 완료되면 블록체인에 연결시킨다
this.chain.push(newBlock);
};
Blockchain.prototype.createGenesisBlock = function () {
//번호 0번, 이전 해시 "0", data를 "GenesisBlock"으로 임의로 지정
return new Block(0, "2021/09/13", "GenesisBlock", "0");
};
Blockchain.prototype.getLatestBlock = function () {
return this.chain[this.chain.length - 1];
};
Blockchain.prototype.isValid = function () {
//제네시스 블록은 이전 블록이 없어 검사를 건너뛰기 위해 1부터 시작한다.
for (let i = 1; i < this.chain.length; i++) {
const currentBlock = this.chain[i];
const prevHash = this.chain[i - 1].hash;
if (currentBlock.prevHash !== prevHash) {
//현재 블록의 이전 해시값이 일치하지 않음
return false;
} else if (currentBlock.calcHash() !== currentBlock.hash) {
//현재 블록에 저장된 해시값과 다시 계산한 해시값이 일치하지 않음
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
//test
const testCoin = new Blockchain();
testCoin.addBlock(new Block(1, "2020/09/14", { foo: "bar" }));
testCoin.addBlock(new Block(2, "2020/09/15", { foo2: "bar2" }));
console.log(testCoin.chain);
난이도를 2로, 즉 해시값이 두개의 0으로 시작하는 값이 나올 때 까지 해싱을 반복한다.
이 경우 첫 번째 채굴에서는 757회의 해시가 발생했고, 41ms가 걸렸다.
엥? 겨우 이정도로 작업 속도를 조절할 수 있다고?
라고 생각할 수 있지만, difficulty를 증가시킬수록 작업 속도는 기하급수적으로 늘어난다.
이번엔 difficulty를 5로 올려보겠다.
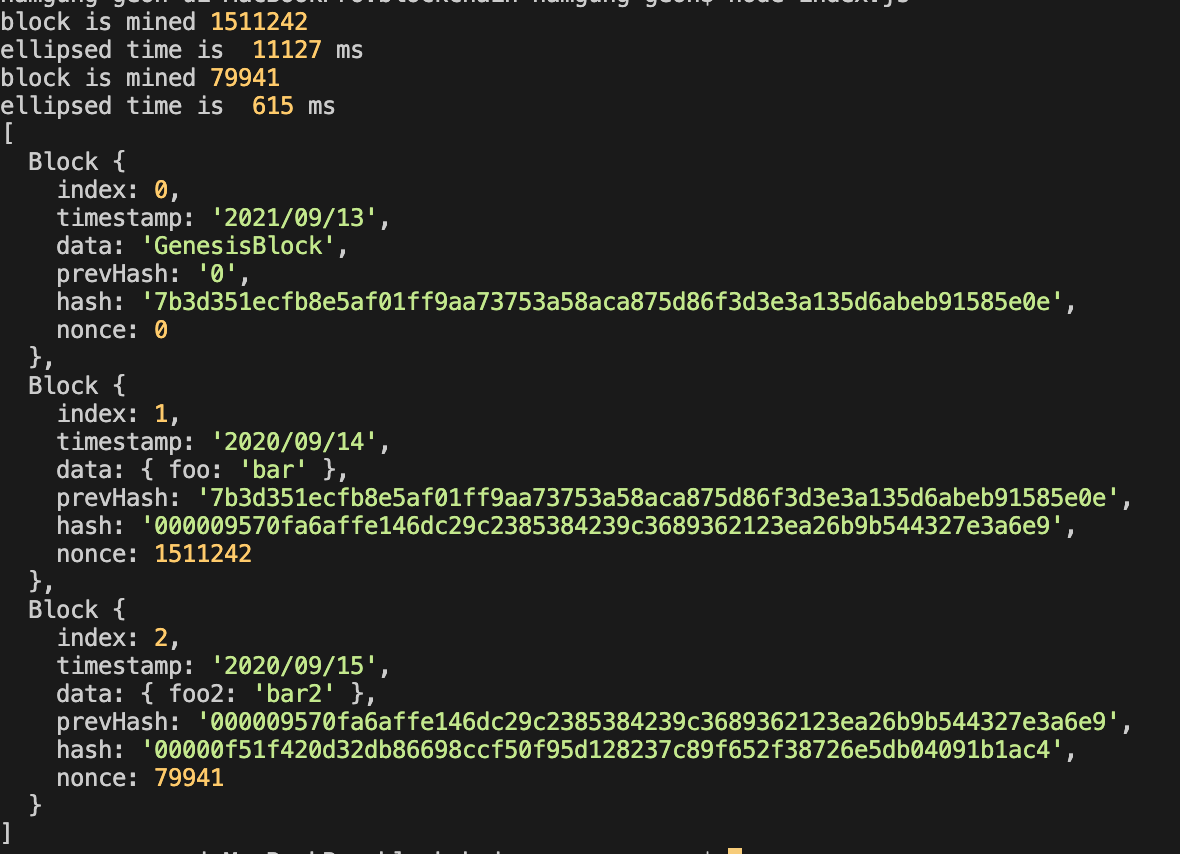
난이도가 3 증가했을 뿐인데, 걸리는 시간은 300배가량 증가했다.
이 원리를 이용해 난이도를 적절히 증가시키면 하나의 새로운 블록을 만드는 데 엄청난 시간이 소요되게 할 수 있으며,
따라서 공격자가 네트워크에 허위 블록을 여러 개 제출하는 행위를 막을 수 있다.
또한 n번째 블록을 변경시키려면, n번째 블록부터 마지막 블록까지의 해시를 전부 계산해야 하므로
불가능할 정도의 엄청난 시간과 비용이 들게 된다.
https://www.coindeskkorea.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=74719
비트코인 채굴 난이도 6% 증가... 5월 이후 처음 올라 - 코인데스크 코리아
비트코인의 채굴 난이도가 6% 증가했다. 중국 정부의 채굴 시장 단속으로 2개월 동안 난이도 하락을 겪은 후 처음으로 상향조정됐다.1일(미국시간) 블록체인 매체 디크립트는 암호화폐 데이터 제
www.coindeskkorea.com
비트코인에서는 이 난이도 값이 14조 가량이 되었다고 한다.
즉, 하나의 블록을 생성하는 데 매우 많은 시간과 컴퓨팅 파워가 요구된다는 것을 알 수 있다.
이 난이도 값은 채굴자가 많은 경우,
다시 말해 새로운 블록을 만들어내는 사람이 많은 경우 증가하여 가짜 블록이 선택되는 일을 방지한다.
다음 포스트에서는 채굴 보상과, 트랜잭션(거래)에 대해 알아볼 것이다.
'BlockChain > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Blockchain] 비트코인 백서 해설 (0) | 2021.12.05 |
|---|---|
| [Blockchain] js로 이해하는 블록체인의 트랜잭션 서명 (Signing Transaction) (0) | 2021.09.15 |
| [Blockchain] js로 이해하는 블록체인의 트랜잭션과 채굴 보상 (Transaction & Mining Reward) (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| [Blockchain] js로 이해하는 블록체인의 기본 구조 (0) | 2021.09.13 |




